√ダウンロード r rna structure 221904-R rna structure and function
Flaviviruses include a diverse group of medically important viruses that cycle between mosquitoes and humans During this natural process of switching hosts, each species imposes different selective forces on the viral population Using dengue virus (DENV) as model, we found that paralogous RNA structures originating from duplications in the viral 3′ untranslated region (UTR) are underRNA or ribonucleic acid is a polymer of nucleotides that is made up of a ribose sugar, a phosphate, and bases such as adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil It plays a crucial role in geneMain Difference – mRNA tRNA vs rRNA mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA are three major types of RNA found in the cell Typically, RNA is a singlestranded molecule, composing of adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil in its structure The pentose sugar is the ribose in all RNA nucleotides RNA is produced by transcription, with the aid of RNA polymerase enzyme Though each RNA type highly vary in their
18s And 28s Ribosomal Rna Secondary Structure Maps Private Website Of Julia Flis
R rna structure and function
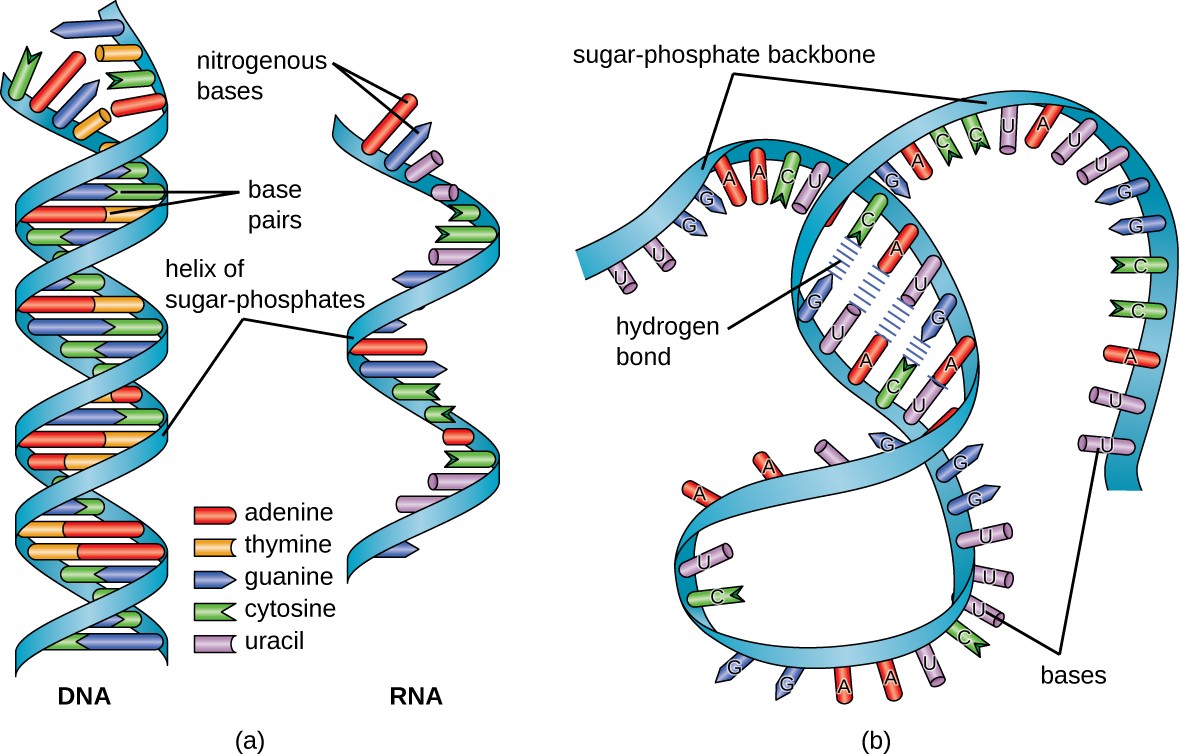
R rna structure and function-RNA Structure RNA is typically single stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by phosphodiester bonds A ribonucleotide in the RNA chain contains ribose (the pentose sugar), one of the four nitrogenous bases (A, U, G, and C), and a phosphate groupRNA Structure RNA is typically single stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by phosphodiester bonds A ribonucleotide in the RNA chain contains ribose (the pentose sugar), one of the four nitrogenous bases (A, U, G, and C), and a phosphate group The subtle structural difference between the sugars gives DNA added stability
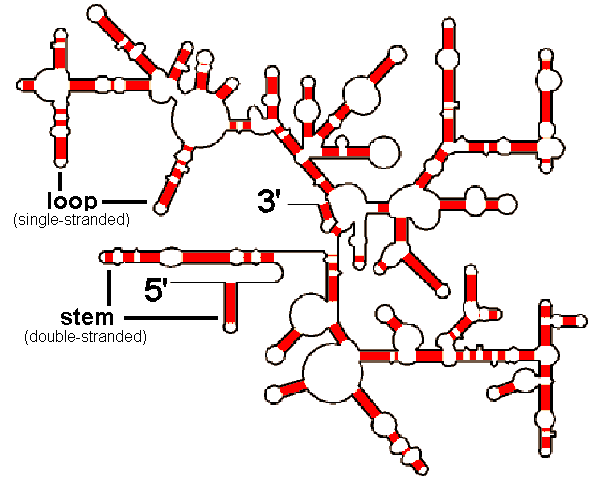


Stems Loops In Rrna
RNAseq analysis in R In this workshop, you will be learning how to analyse RNAseq count data, using R This will include reading the data into R, quality control and performing differential expression analysis and gene set testing, with a focus on the limmavoom analysis workflowIts new version, RNApdbee , is a highly advanced multifunctional tool for RNA structure annotation, revealing the relationship between RNA secondary and 3D structure given in the PDB or PDBx/mmCIF format The upgraded version incorporates new algorithms for recognition and classification of highordered pseudoknots in large RNA structuresRNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a linear polymer of adenine, thymine, cytosine, and uracil that is created in the cell by a process called transcription, and it differs from DNA in several ways First, the ribose sugars on DNA nucleotides are short one hydroxyl group compared to RNA, hence the name deoxyribonucleic acid
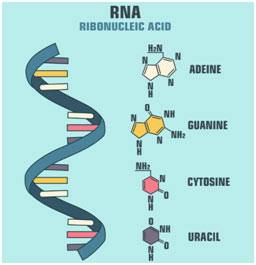
The Darm plays a major role in stabilizing the structure of RNA;RNA A polymer of ribonucleotides, is a single stranded structure There are three major types of RNA m RNA,t RNA and r RNA Besides that there are small nuclear,micro RNAs, small interfering and heterogeneous RNAs Each of them has a specific structure and performs a specific functionBasic Structure of RNA The basic structure of RNA is shown in the figure belowThe ribonucleic acid has all the components same to that of the DNA with only 2 main differences within it RNA has the same nitrogen bases called the adenine, Guanine, Cytosine as that of the DNA except for the Thymine which is replaced by the uracil
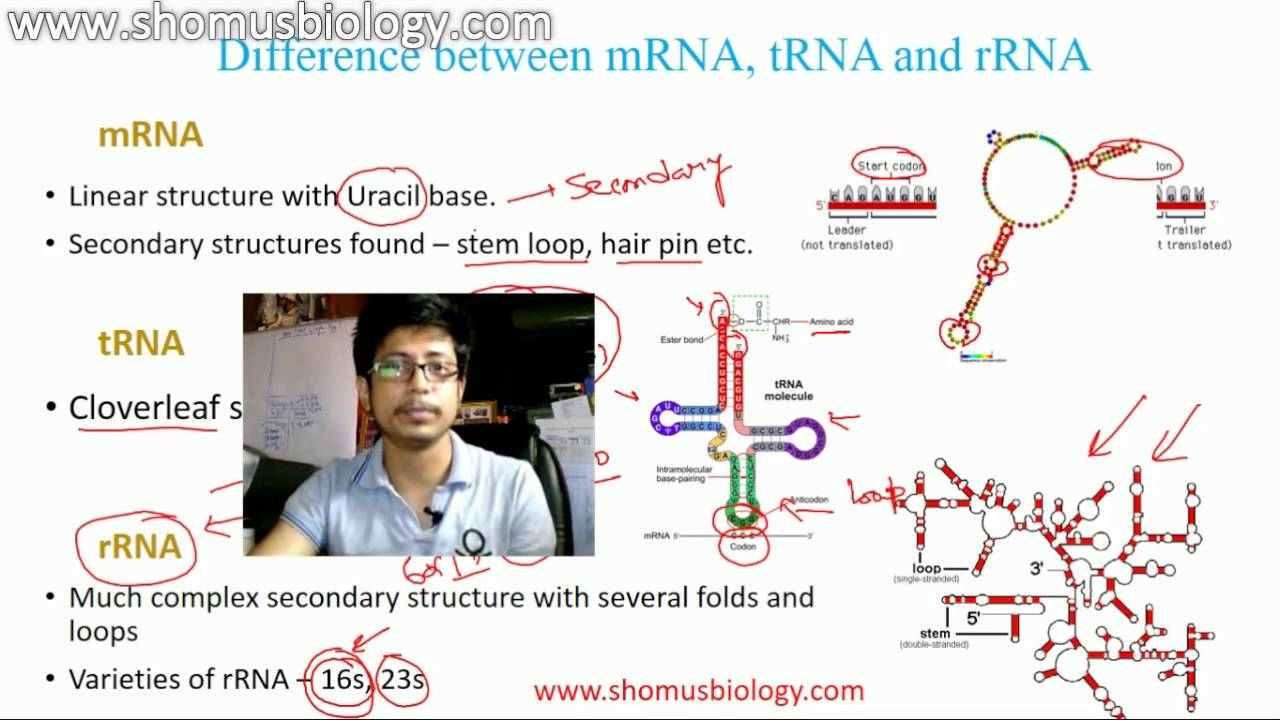
The RNA is ribonucleic acid, tRNA, rRNA and mRNA are three different types of RNA present in a cellThe structure of the RNA molecule was described by RW Holley in 1965 RNA structure RNA typically is a singlestranded biopolymer However, the presence of selfcomplementary sequences in the RNA strand leads to intrachain basepairing and folding of the ribonucleotide chain into complex structural forms consisting of bulges and helicesIts new version, RNApdbee , is a highly advanced multifunctional tool for RNA structure annotation, revealing the relationship between RNA secondary and 3D structure given in the PDB or PDBx/mmCIF format The upgraded version incorporates new algorithms for recognition and classification of highordered pseudoknots in large RNA structures


18s And 28s Ribosomal Rna Secondary Structure Maps Private Website Of Julia Flis



Sequence And Secondary Structure Of The Mitochondrial 16s Ribosomal Rna Gene Of Ixodes Scapularis Sciencedirect
RNA is a singlestranded nucleic acid that is composed of three main elements a nitrogenous base, a fivecarbon sugar and a phosphate group Messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are the three major types of RNAMichelle R McGehee, in Molecular Biology (Third Edition), 19 Abstract Noncoding RNA refers to all those RNA molecules that play biological roles as RNA, rather than being translated into protein like messenger RNA Transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA take part in protein synthesis Occasional RNA molecules act catalytically, as RNA enzymesAn R loop is a special triplestranded nucleic acid structure formed when nascent RNA invades doublestranded DNA (dsDNA) during transcription, resulting in a DNARNA hybrid and a displaced singlestranded DNA (ssDNA)



E Coli Ribosomal Rna Rrna Structure Derived From Pdb Structure 3j7z
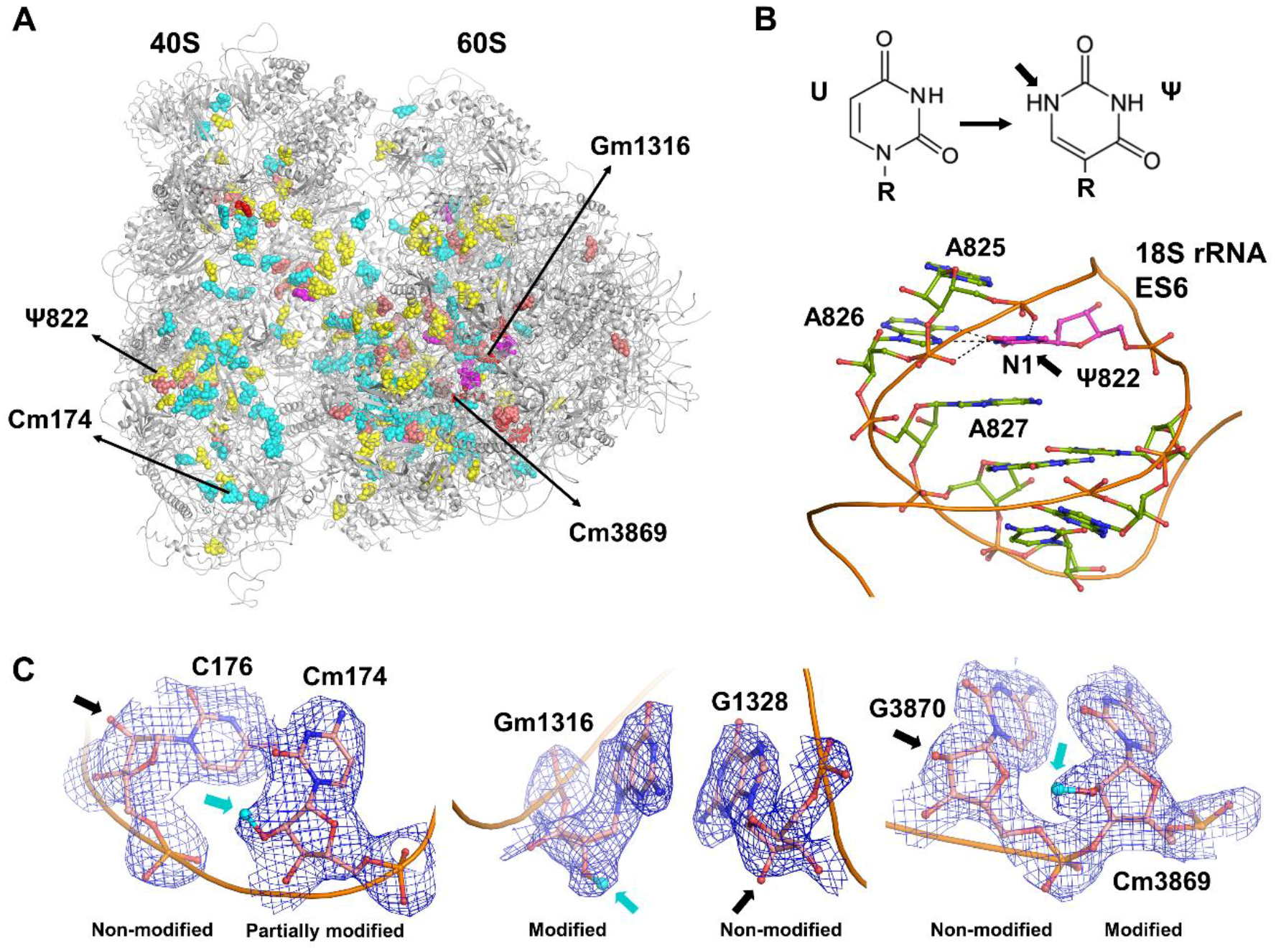


Biomolecules Free Full Text Visualizing The Role Of 2 Oh Rrna Methylations In The Human Ribosome Structure Html
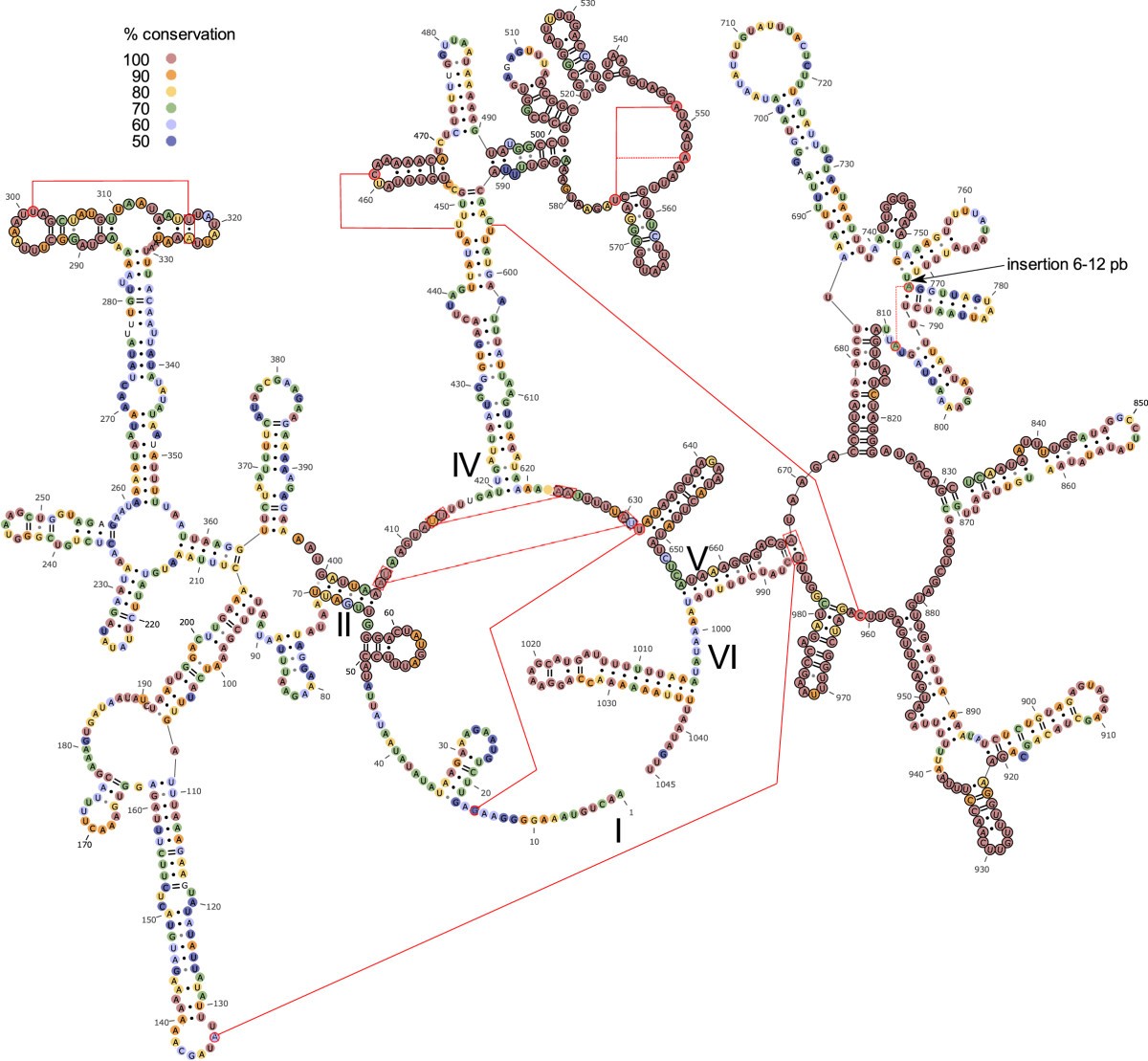
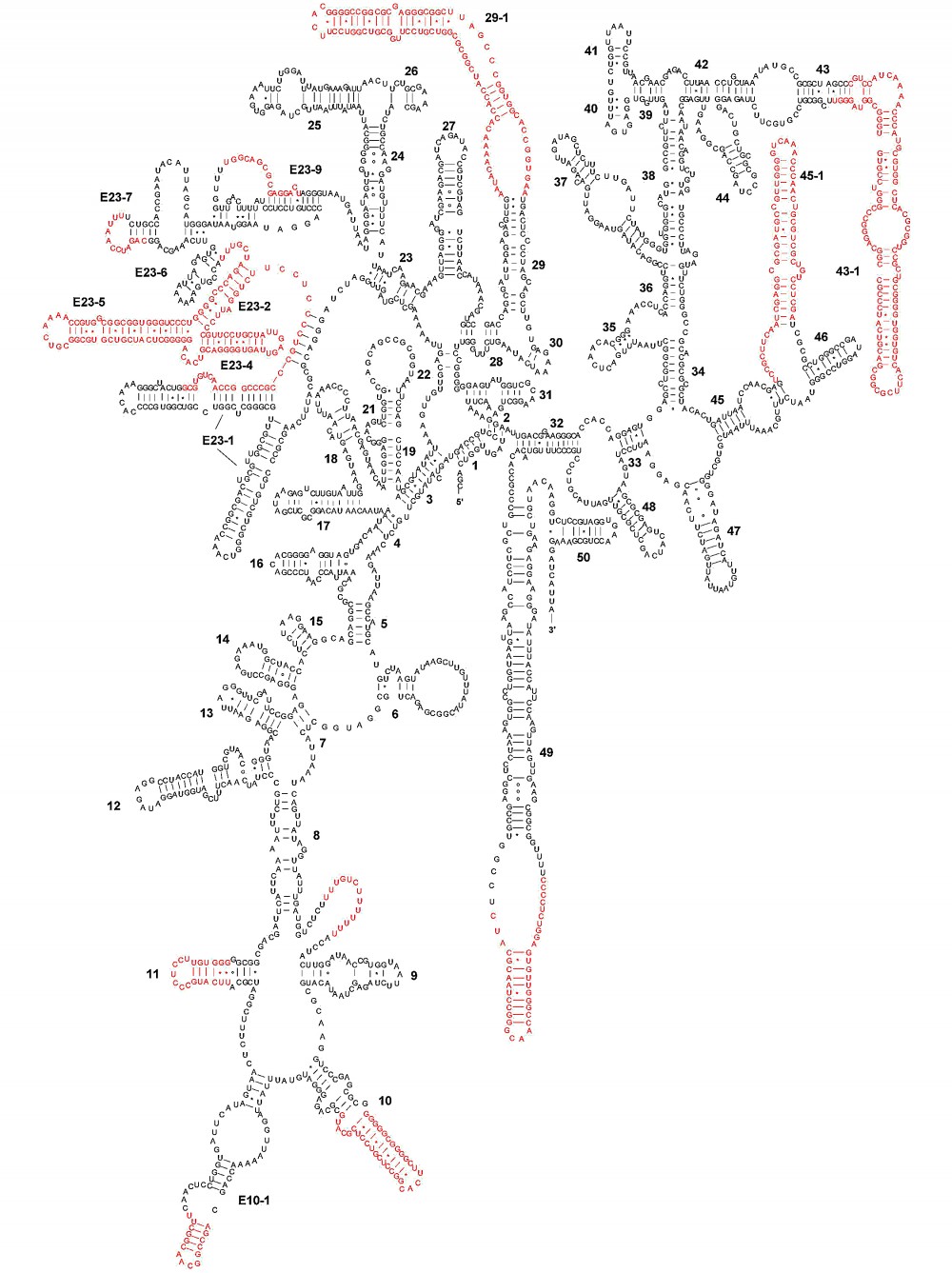
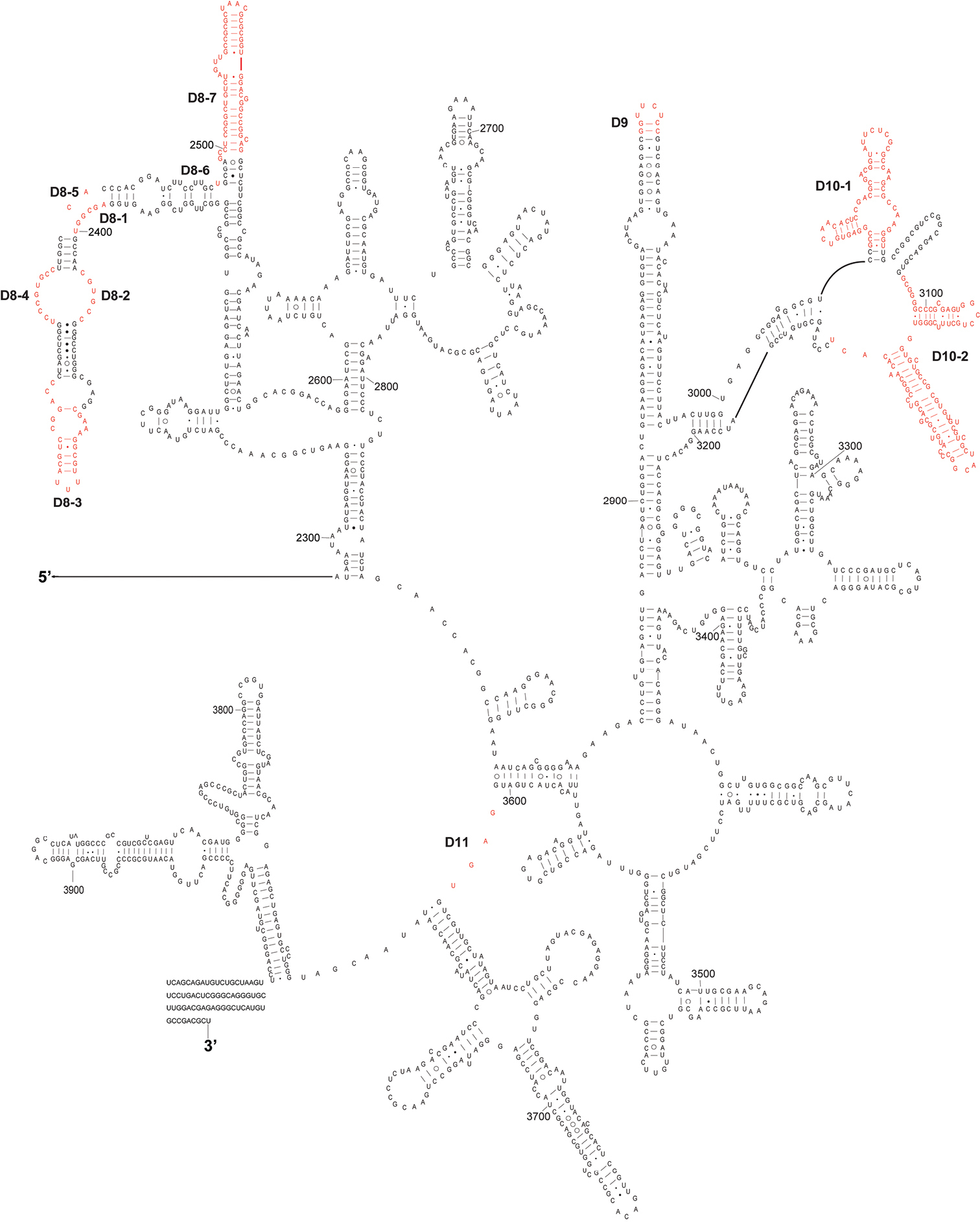
RNA and ribonucleoprotein particles (RNPs) are involved in a large number of cellular processes for which intricate tertiary structures are often required As a consequence of base pairing and higher order interactions, RNA molecules can form preferred secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structuresThe secondary structure of 16S rRNA is shown in figure 1 Figure 1 16S rRNA The 3'end of the 16S rRNA contains the antiShineDalgarno sequence that binds upstream to the start codon, AUG The ShineDalgarno sequence is the ribosomal binding site of the bacterial mRNA As 16S rRNA is essential for the functioning of the bacteria, the geneResults Structure of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA, as Predicted by a BestofCategory Algorithm We focused on 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) because its structure is known and it contains numerous typical RNA motifs (14, 15)We predicted the secondary structure of 16S rRNA by using the program RNAstructure (), whose algorithm is among the most accurate currently available ()


Rna Structure And Function



Diversity Of 16s Rrna Genes Within Individual Prokaryotic Genomes Applied And Environmental Microbiology
RNAstructure, Version 62 Updated November 27, 19 () RNAstructure is a complete package for RNA and DNA secondary structure prediction and analysis It includes algorithms for secondary structure prediction, including facility to predict base pairing probabilitiesRNA has a simpler structure and is needed in order for DNA to function Also, RNA is found in prokaryotes, which are believed to precede eukaryotes RNA on its own can act as a catalyst for certain chemical reactions The real question is why DNA evolved if RNA existed The most likely answer for this is that having a doublestranded moleculeRchie allows you to make arc diagrams of RNA secondary structures, allowing for easy comparison and overlap of two structures, rank and display basepairs in colour and to also visualize corresponding multiple sequence alignments and covariation information R4RNA is the R package powering Rchie, available for download and local use for more customized figures and scripting
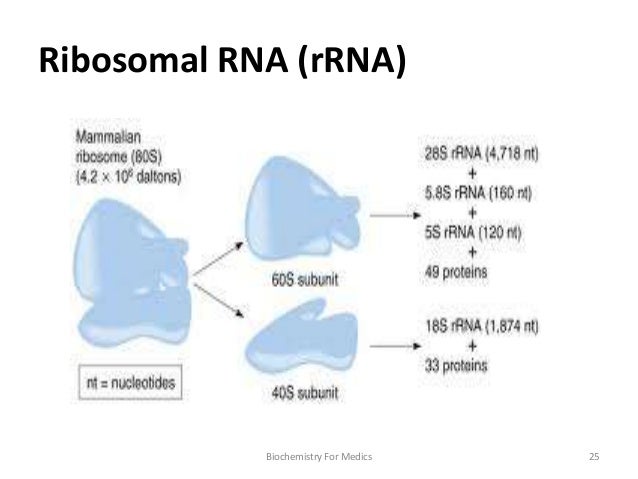


Rna Structure Types And Functions



Rrna Binding Sites And The Molecular Mechanism Of Action Of The Tetracyclines Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy
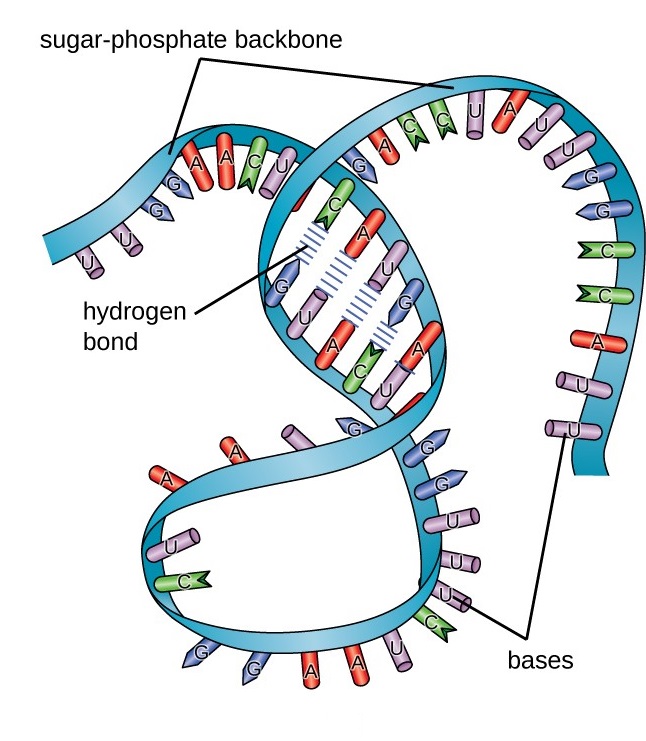
RNA regulation is significantly dependent on its binding protein partner, known as the RNAbinding proteins (RBPs) Unfortunately, the binding preferences for most RBPs are still not well characterized Interdependencies between sequence and secondary structure specificities is challenging for both predicting RBP binding sites and accurate sequence and structure motifs detectionStandard RNA secondary structure prediction tools such as mfold and RNAfold (Table 4) are based on the calculation of the minimum free energy (MFE) and can fold reliably on small local windows of up to 300 nt Secondary structures of larger genomic segments or interactions spanning larger regions, including pseudogenes, are stillUnlike doublestranded helical structure of DNA, the RNAs are singlestrandedRNA is an unbranched linear polymer of ribonucleotides joined by 3′, 5′ phosphodiester bonds The phosphodiester bonds join with the 3′ OH group of ribose of one nucleotide group to the 5′ OH group of ribose sugar of the next nucleotide



Location Of M3u Methylations In The Ribosomal Rna A 3d Cartoon Of Download Scientific Diagram



Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology
Ribosomal RNA are transcribed in the nucleus, at specific structures called nucleoli These are dense, spherical shapes that form around genetic loci coding for rRNA Nucleoli are also crucial for the eventual biogenesis of ribosomes, through sequestration of ribosomal proteins Discovery of Ribosomal RNAAn RNA strand can undergo significant intramolecular base pairing to take on a threedimensional structure During transcription , the information encoded in DNA is used to make RNA RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA, using the antisense strand of the DNA as template by adding complementary RNA nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strandRNA STRUCTURE Like DNA, RNA is a long polymer consisting of nucleotides RNA is a singlestranded helix The strand has a 5′end (with a phosphate group) and a 3′end (with a hydroxyl group) It is composed of ribonucleotides The ribonucleotides are linked together by 3′ –> 5′ phosphodiester bonds



Figure 2 From The Secondary Structure Of Human 28s Rrna The Structure And Evolution Of A Mosaic Rrna Gene Semantic Scholar



Ribosome Biogenesis In The Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Genetics
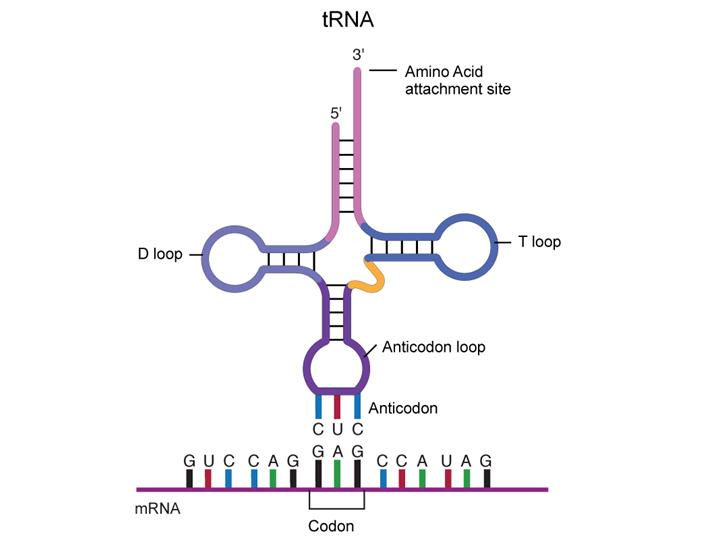
The rRNAs form extensive secondary structures Molecules of rRNA are synthesized in a specialized region of the cell nucleus called the nucleolus, which appears as a dense area within the nucleus and contains the genes that encode rRNA The encoded rRNAs differ in size, being distinguished as either large or smallThe tertiary structure creates two double helices at right angle to each other The amino acid binding site is opposite to the anticodon arm This facilitates protein synthesis The tRNA constitutes about 10% of the total cellular RNA RNA Type # 2 Messenger RNA (mRNA) Messenger RNA is a linear molecule transcribed from one strand of DNAThe RNA is a ribonucleic acid made up of the ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose sugar of the DNA For more detail, on RNA you can read our article on RNA RNA Structure and Function First, let me brief you the RNA;
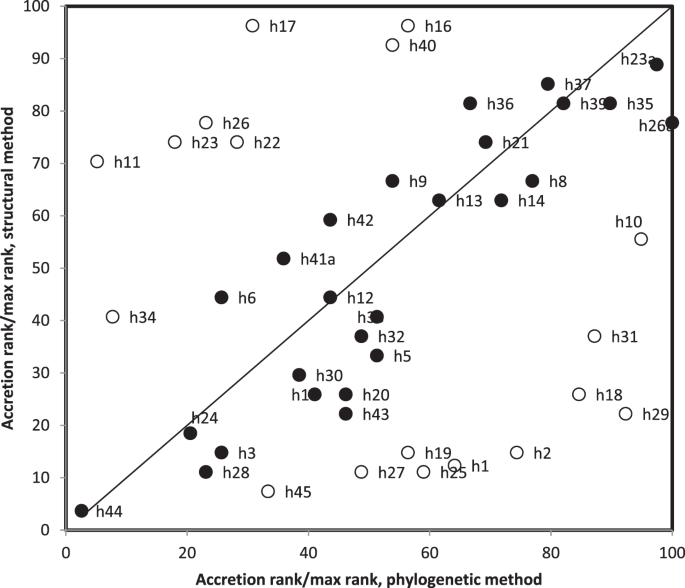


Comparisons Between Small Ribosomal Rna And Theoretical Minimal Rna Ring Secondary Structures Confirm Phylogenetic And Structural Accretion Histories Scientific Reports



Astrobiology In The Folds Astrobiology Magazine
RNA can be found in singlestranded form, but it more commonly forms complex threedimensional structures, and this feature usually serves to confer functionality on RNA molecules RNA Synthesis RNA transcription is a process mediated by RNA polymerase, an enzyme that creates an RNA complement to template DNA with the help of a complex of proteinsTheir functionality is seemingly endless Throughout the latter half of the th century, we believed that RNA's primary role was to intermediate between DNA and protein, as we described aboveRNAstructure, Version 62 Updated November 27, 19 () RNAstructure is a complete package for RNA and DNA secondary structure prediction and analysis It includes algorithms for secondary structure prediction, including facility to predict base pairing probabilities
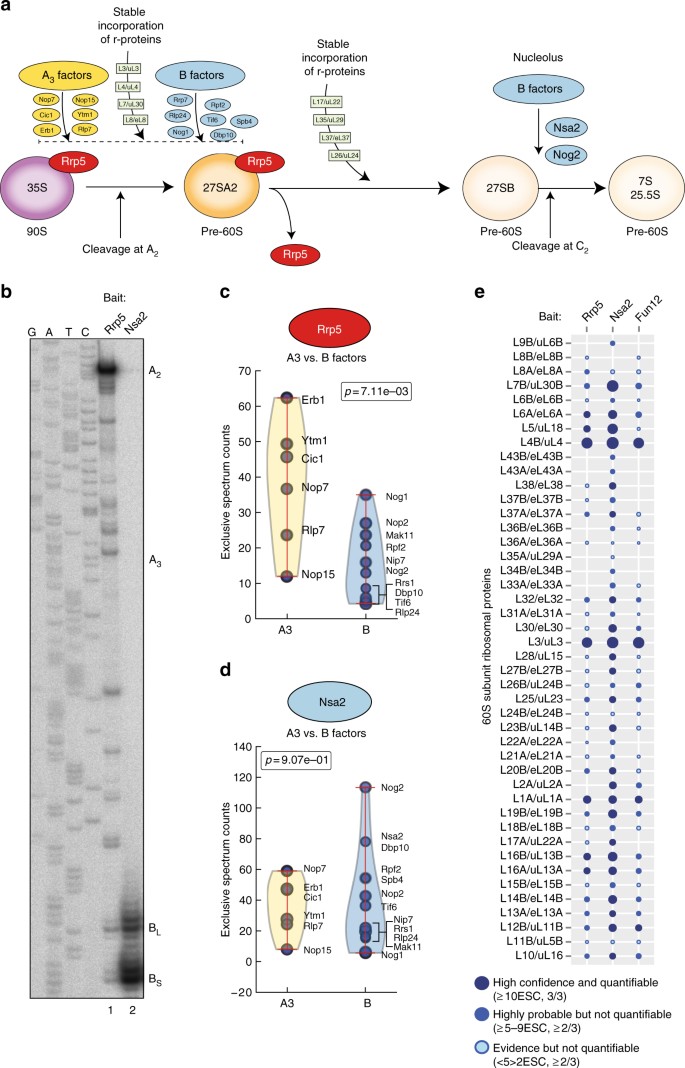


High Throughput Rna Structure Probing Reveals Critical Folding Events During Early 60s Ribosome Assembly In Yeast Nature Communications


Full Article
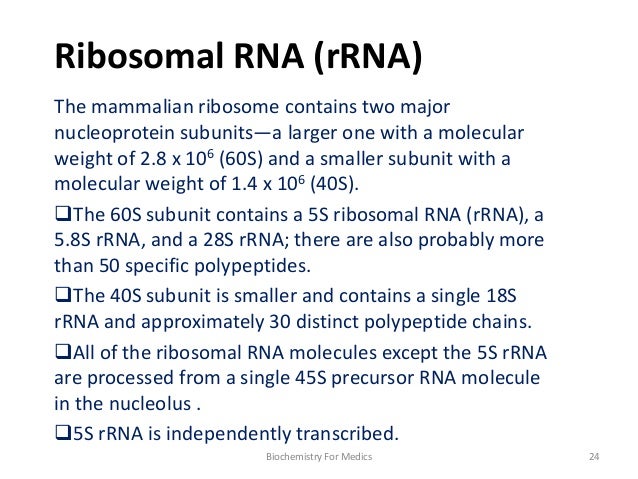
Predict the lowest free energy structure and a set of low free energy structures for a sequence MaxExpect Generate a structure or structures composed of highly probable base pairs This is an alternative method for structure prediction that may have higher fidelity in structure prediction MultilignRNA is genomic (genetic) in some viruses like TMV, HIV influenza virus etc It is double stranded in reoviruses, wound tumor virus, Rice Dwarf virus and Mycophages 1 Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) It is the most abundant RNA (7080% of total) which has 34 types Some of its types (23S, 28S) are the longest of all RNAsThe structure of the small subunit of eukaryotic rRNA has been discovered Synthesis RNA polymerase is the protein that makes the copy of DNA Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)


18s And 28s Ribosomal Rna Secondary Structure Maps Private Website Of Julia Flis
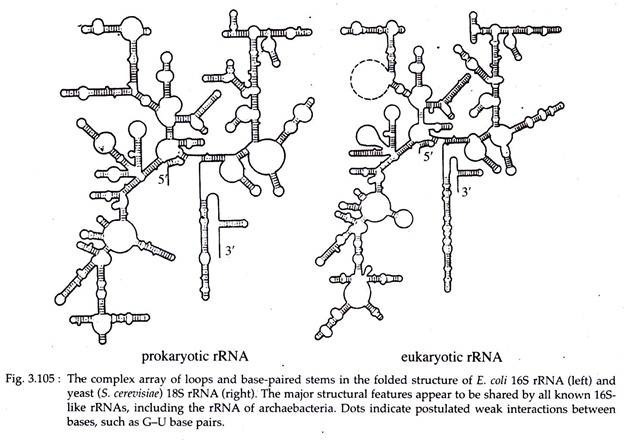


Rna Structure Classes And Properties Nucleic Acid
It affects and influences the kinetics and accuracy of translation at the ribosomes The Tarm also influences the tRNA effect on the translation by interaction with the ribosomes The Darm, Tarm, and the anticodon loop combined resembles a cloverleafRRNA is the heaviest RNA having high molecular weight (> 1000 KD) and accounts for 80% of the total RNA in a cell It exists in secondary structure in which single strand coils and folds up on itself, however, overall structure of rRNA differs from one another rRNAs are the structural components of the ribosomes , hence called ribosomal RNARNA at a first glance appears to be very similar to DNA, has its own distinctive structural features It is a singlestranded molecule with an intrastrand pairing RNA exhibits an extensive double helical structure and can also form various tertiary structures The general structure of RNA



Secondary Structure Of The Human 18s Rrna Showing Differences In Dms Download Scientific Diagram



Cryo Em Structure Of The Rna Rich Plant Mitochondrial Ribosome Biorxiv
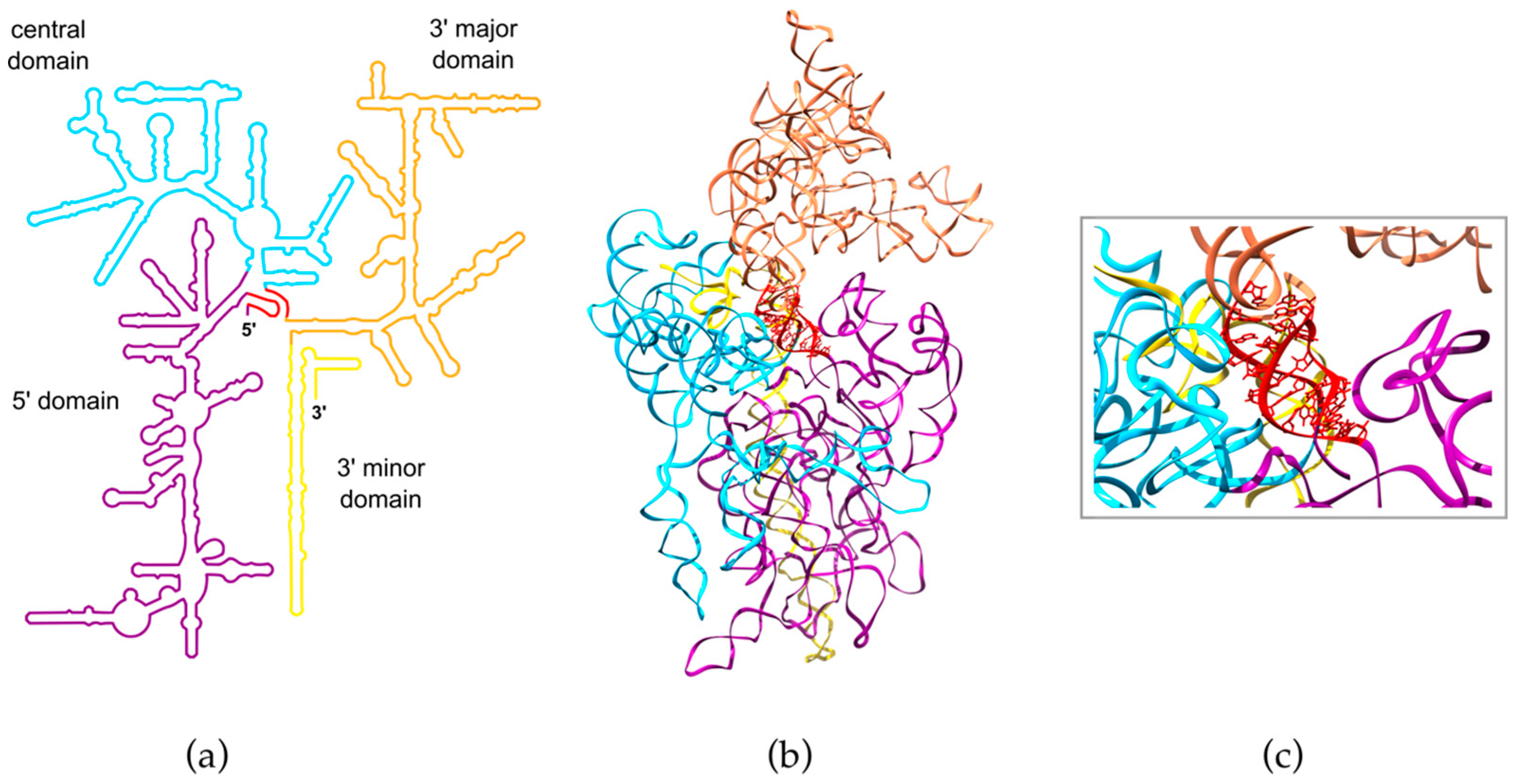
The tertiary structure of the small subunit ribosomal RNA (SSU rRNA) has been resolved by Xray crystallography The secondary structure of SSU rRNA contains 4 distinct domains—the 5', central, 3' major and 3' minor domains A model of the secondary structure for the 5' domain ( nucleotides) is shown BiosynthesisStructure and function of ribosomal RNA Biochem Cell Biol NovDec 1995;73(1112) doi /o Authors H F Noller 1 , R Green, G Heilek, V Hoffarth, A Hüttenhofer, S Joseph, I Lee, K Lieberman, A Mankin, C Merryman, et al Affiliation 1 Center forProteins are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs;
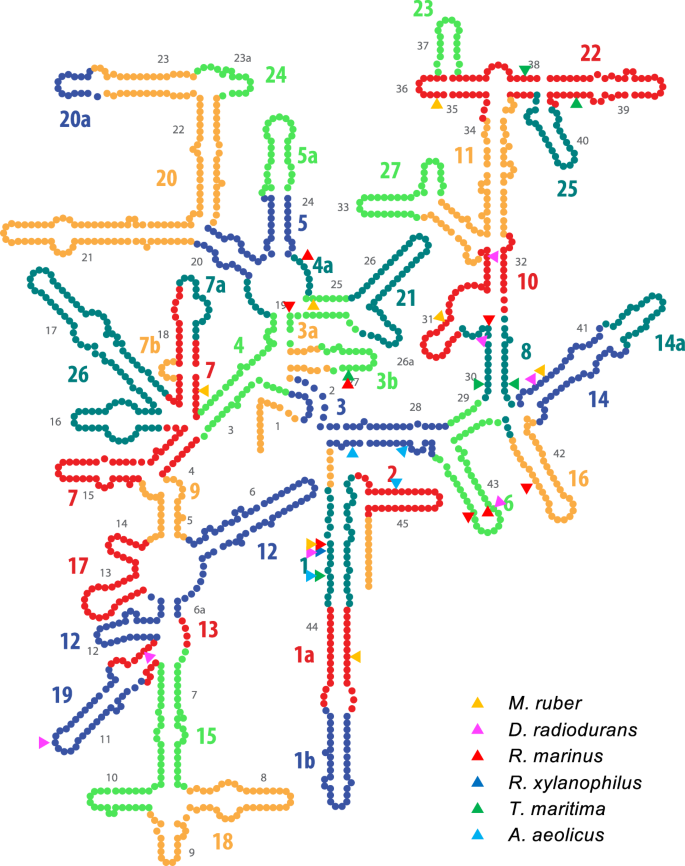


Occurrence Of Randomly Recombined Functional 16s Rrna Genes In Thermus Thermophilus Suggests Genetic Interoperability And Promiscuity Of Bacterial 16s Rrnas Scientific Reports



Protein Synthesis Ribosomes 16s Rrna Secondary Structures Ppt Download
DNA makes RNA that leads to proteins Therefore, proteins are regarded as the workhorses of the cell, that play essential roles in the cellKladwang, W, Chou, FC, and Das, R (12) "Automated RNA structure prediction uncovers a kinkturn linker in double glycine riboswitches" Journal of the American Chemical Society 134 (3) 1404 1407 Paper Link ModelsMost of the existing random generation algorithms for RNA secondary structures are used for predicting the structure of a given RNA sequence (see eg 6,7), while others can be employed for instance for evaluating structure comparison softwares Note that secondary structure prediction methods based on random sampling represent a nondeterministic counterpart to the uptodate most


Chlamydomonas Reinhardtii Ssu Rrna Secondary Structure Model



Rna Structure Reading The Ribosome Science
From DNA to RNA transcription (Part 9 of 10) Playlist link http//wwwyoutubecom/playlist?list=PL4554CB8DF400E44A Transcript link Related article BigRNAs take part in the protein synthesis There are three different types of RNAs present in a cell, namely mRNA or messenger RNA, rRNA or ribosomal RNA and tRNA or transfer RNA They are named according to the function they perform Each of the three types of RNAs performs unique functions and have different structuresAn RNA virus is a virus that has RNA (ribonucleic acid) as its genetic material This nucleic acid is usually singlestranded RNA but may be doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, COVID19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles


Genes Iv Index Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis 6 12 The Organization Of 16s Rrna The Ribosome Was Originally Viewed As A Collection Of Proteins With Various Catalytic Activities Held Together By Protein Protein Interactions And By Binding To Rrna



Structure Of Escherichia Coli Ribosomal Protein L25 Complexed With A 5s Rrna Fragment At 1 8 A Resolution Pnas
RRNA is the heaviest RNA having high molecular weight (> 1000 KD) and accounts for 80% of the total RNA in a cell It exists in secondary structure in which single strand coils and folds up on itself, however, overall structure of rRNA differs from one another rRNAs are the structural components of the ribosomes , hence called ribosomal RNACleavage of transfer (t)RNA and ribosomal (r)RNA are critical and conserved steps of translational control for cells to overcome varied environmental stresses However, enzymes that are responsible for this event have not been fully identified in high eukaryotes Here, we report a mammalian tRNA/rRNThe chemical structure of RNA is very similar to that of DNA, but differs in three primary ways Unlike doublestranded DNA, RNA is a singlestranded molecule in many of its biological roles and consists of much shorter chains of nucleotides However, a single RNA molecule can, by complementary base pairing, form intrastrand double helixes, as in tRNA



Figure 3 From Structure Of Ribosomal Rna Semantic Scholar
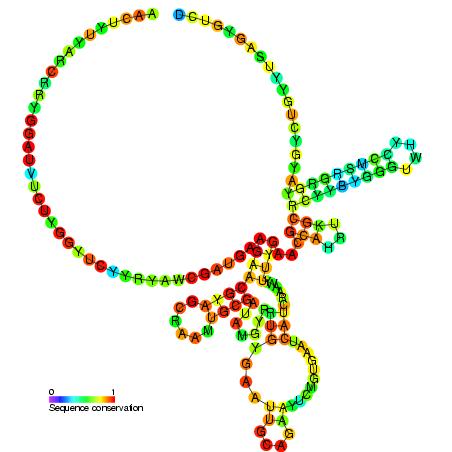


5 8s Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia
In the year 1965, RW Holley described the RNA structure The essential and significant process of molecular biology is the flow of genetic information in a cell, which is three steps;RNA A polymer of ribonucleotides, is a single stranded structure There are three major types of RNA m RNA,t RNA and r RNA Besides that there are small nuclear,micro RNAs, small interfering and heterogeneous RNAs Each of them has a specific structure and performs a specific function



Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia


Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology



Rna Seq With Rnase H Based Ribosomal Rna Depletion Specifically Designed For C Elegans



5s Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia


Palaeos Eukarya Glossary P T



A Overview Of The Human 80s Ribosome Structure With Rrna Download Scientific Diagram


Q Tbn And9gct4sntp1bmgsmuiukn0qlotkbs2zg2az0c2qa6u0sxazxxv Usqp Cau


Rna Structure Types And Functions


Secondary Structure Models Of 18s And 28s Rrnas Of The True Bugs Based On Complete Rdna Sequences Of Eurydema Maracandica Oshanin 1871 Heteroptera Pentatomidae
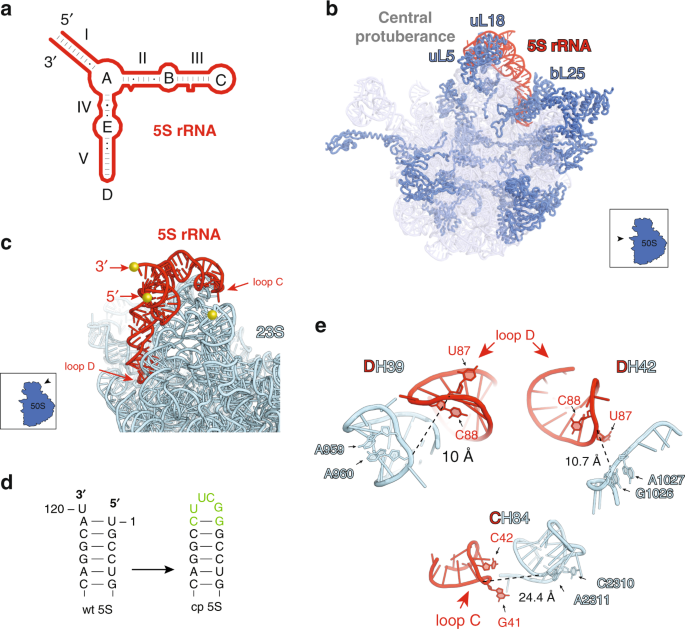


Ribosome Engineering Reveals The Importance Of 5s Rrna Autonomy For Ribosome Assembly Nature Communications


Plos One A Comparison Of The Crystal Structures Of Eukaryotic And Bacterial Ssu Ribosomal Rnas Reveals Common Structural Features In The Hypervariable Regions



Secondary Structure Of The Human Lsu Mt Rrna Modified From Brown Et Download Scientific Diagram



Incorporating Chemical Modification Constraints Into A Dynamic Programming Algorithm For Prediction Of Rna Secondary Structure Pnas


18s And 28s Ribosomal Rna Secondary Structure Maps Private Website Of Julia Flis



Ribosomal Rna Definition Function Britannica



Rna Structure Function Section 12 3 Pp Ppt Download
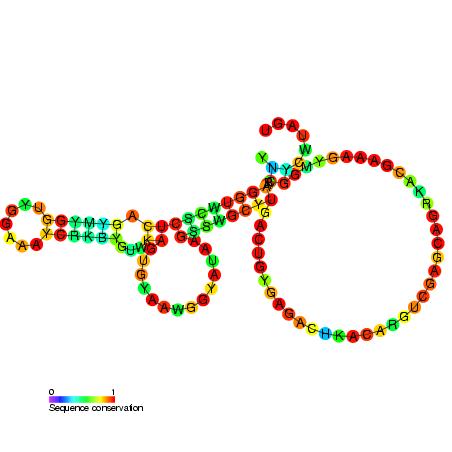


23s Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia


Ribosome Images


Article


14 2 Overview Of Transcription Biology Libretexts
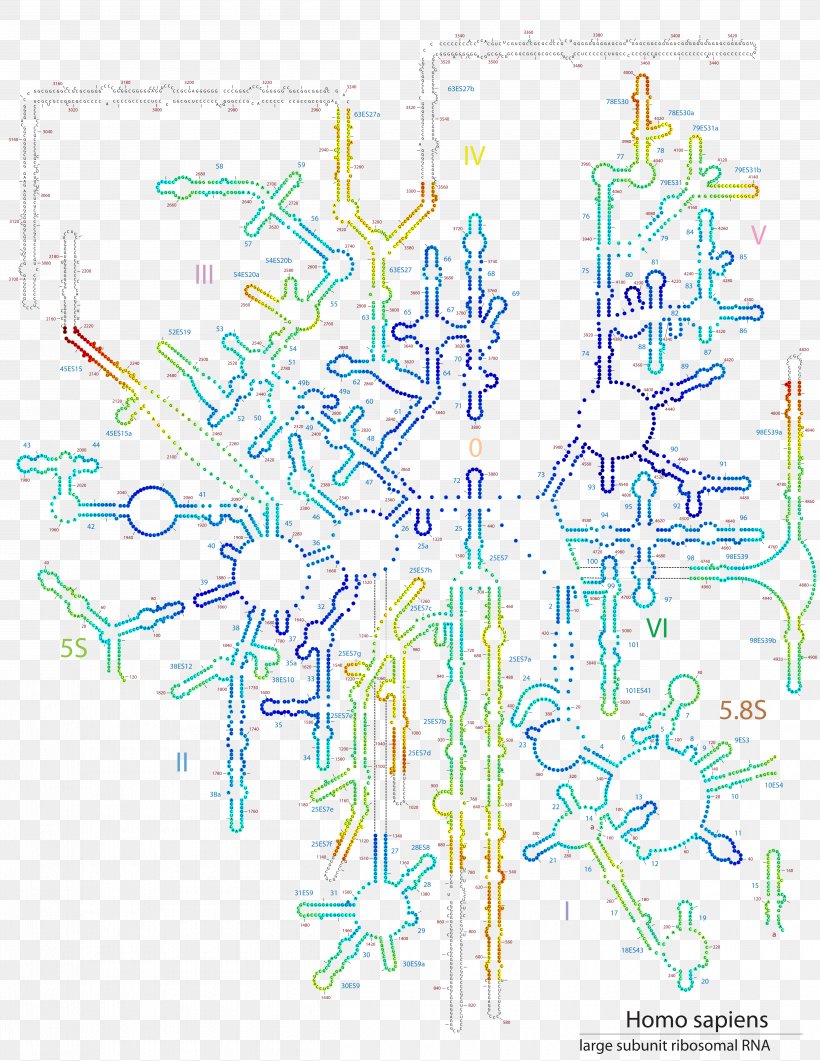


28s Ribosomal Rna Ribosome Protein Secondary Structure Png 5000x6471px Ribosomal Rna Area Biomolecular Structure Cryogenic Electron
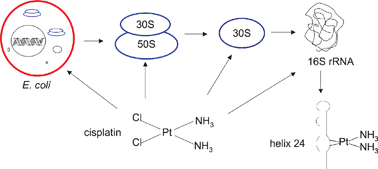


A New Role For Cisplatin Probing Ribosomal Rna Structure Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing
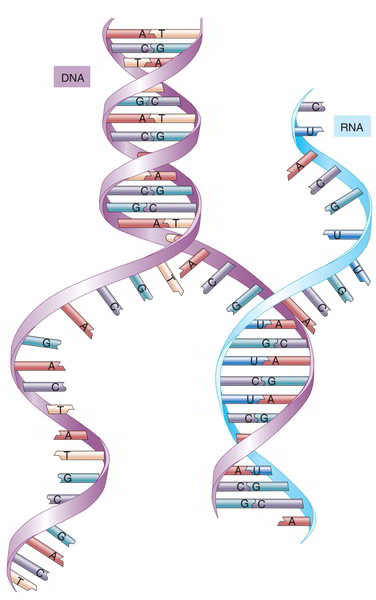


Rna Structure Function Synthesis Types And Interference Earth S Lab


Difference Between Mrna Trna And Rrna Knowswhy Com


8
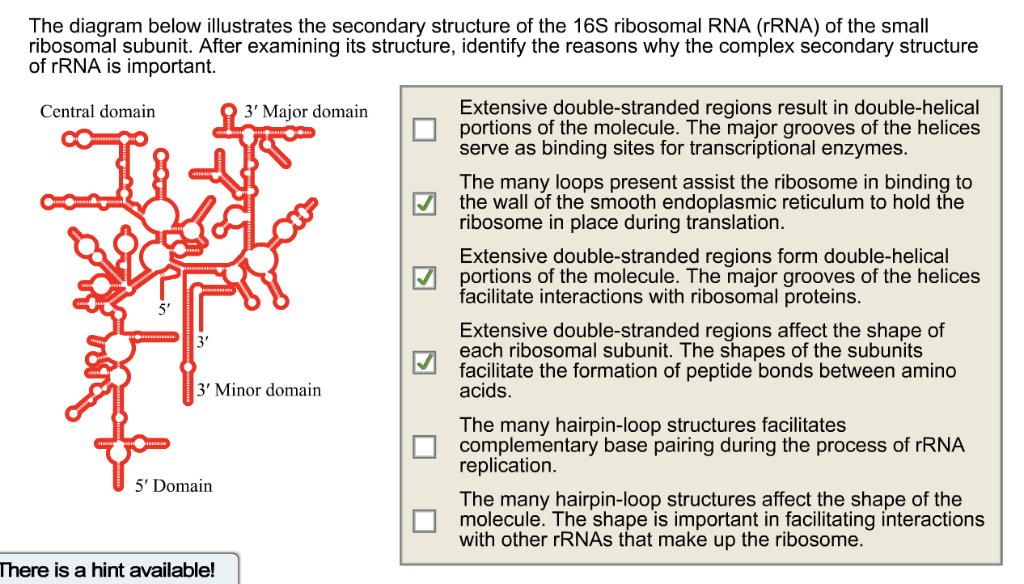


Solved The Diagram Below Illustrates The Secondary Struct Chegg Com



Stems Loops In Rrna
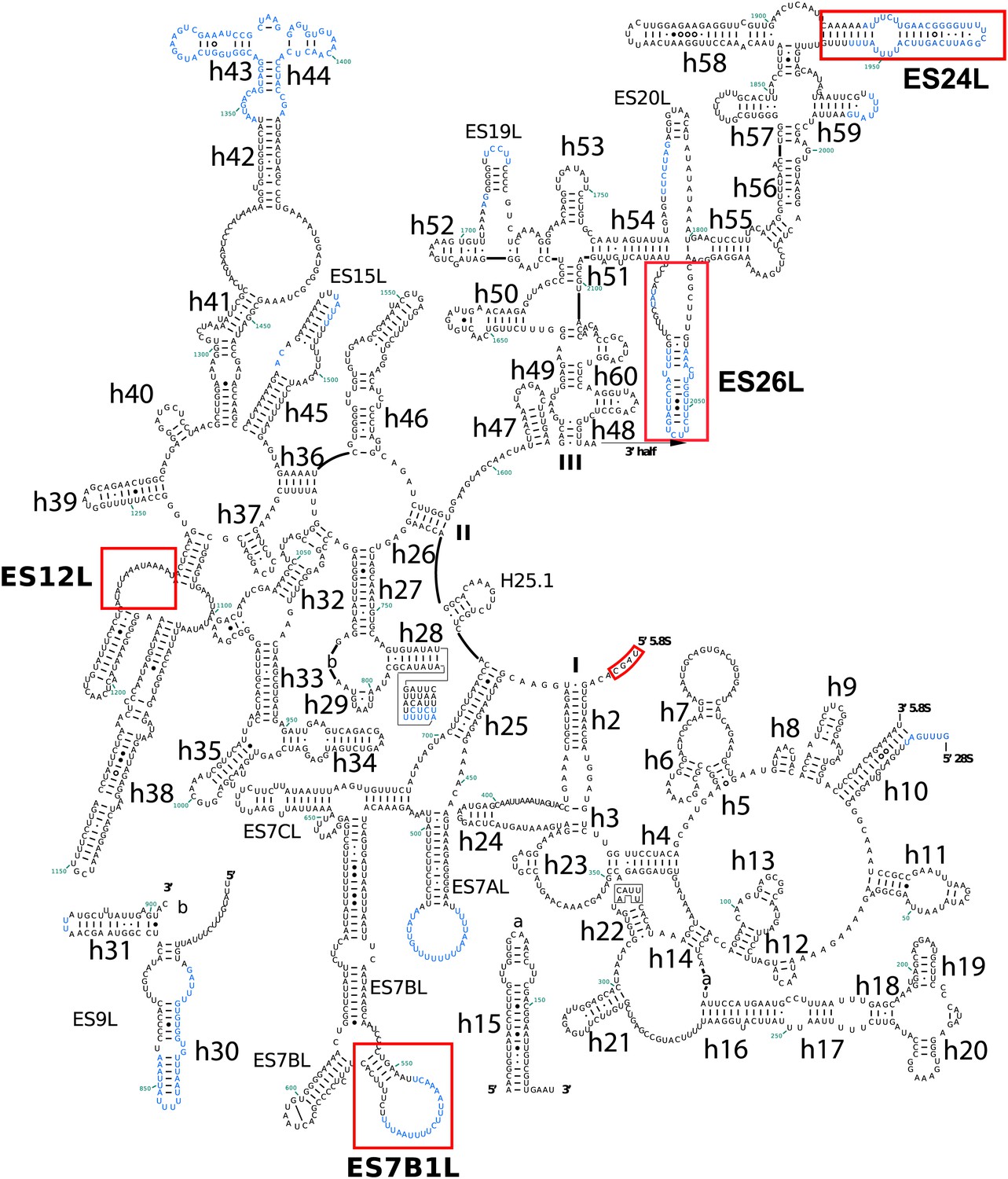


Cryo Em Structure Of The Plasmodium Falciparum 80s Ribosome Bound To The Anti Protozoan Drug Emetine Elife
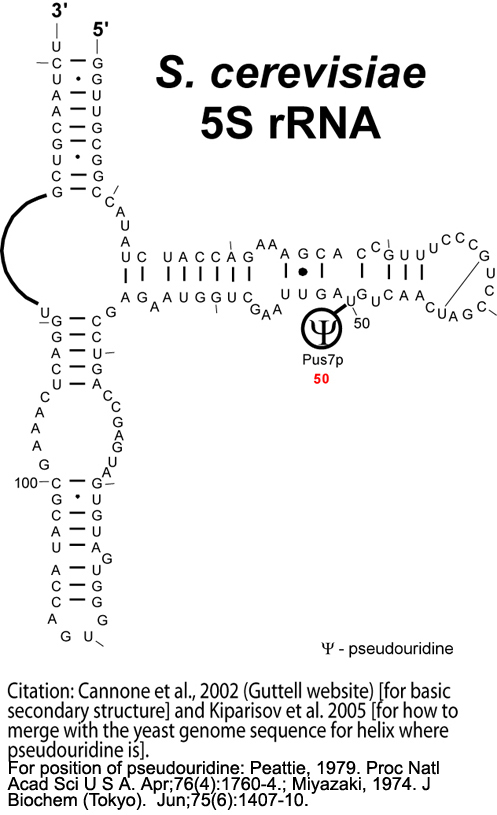


5s Rrna Seconadry Structure Map



Rna Structure Reading The Ribosome Science



A Single N1 Methyladenosine On The Large Ribosomal Subunit Rrna Impacts Locally Its Structure And The Translation Of Key Metabolic Enzymes Biorxiv
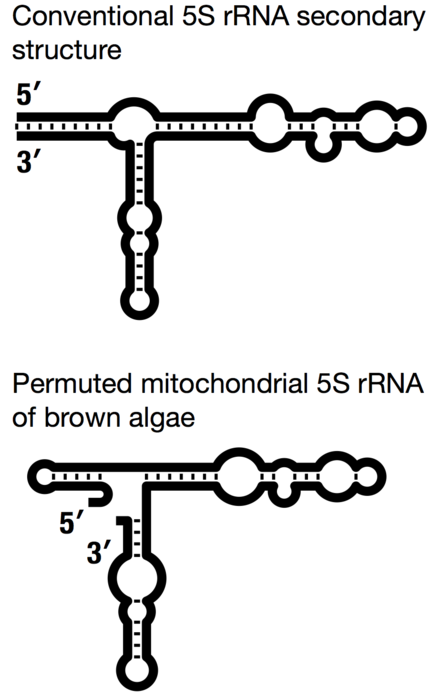


5s Ribosomal Rna Wikiwand


Rna Structure Types Mrna Trna Rrna And Functions


Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network


Mrna Trna And Rrna Youtube


Next Generation Sequencing Phylogenetic Signal And Comparative Mitogenomic Analyses In Metacrangonyctidae Amphipoda Crustacea Bmc Genomics Full Text


18s Rrna Secondary Structure Acanthamoeba And Free Living Amoebae


Secondary Structure Models Of 18s And 28s Rrnas Of The True Bugs Based On Complete Rdna Sequences Of Eurydema Maracandica Oshanin 1871 Heteroptera Pentatomidae


3


Plos One Optimization Of Ribosome Structure And Function By Rrna Base Modification



Ribosomal Rna Definition Function Britannica


Biomolecules Free Full Text Pre Ribosomal Rna Processing In Human Cells From Mechanisms To Congenital Diseases Html



Transient Protein Rna Interactions Guide Nascent Ribosomal Rna Folding Sciencedirect



Dr Jennifer Blm Staythef Ckhome Glass My Latest Sciart Creation A Cross Stitch Needlepoint Of The Secondary Structure Of 16s Ribosomal Rna One Of The Most Ancient And Most Conserved Biomolecules On



Ribosomal Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Secondary Structure Model For Prokaryotic 16s Rrna Regions Where The Download Scientific Diagram



Ribosomal Rna Rrna Definition Function Biology Dictionary


Rna Properties Structure Types And Functions Molecular Biology Microbe Notes
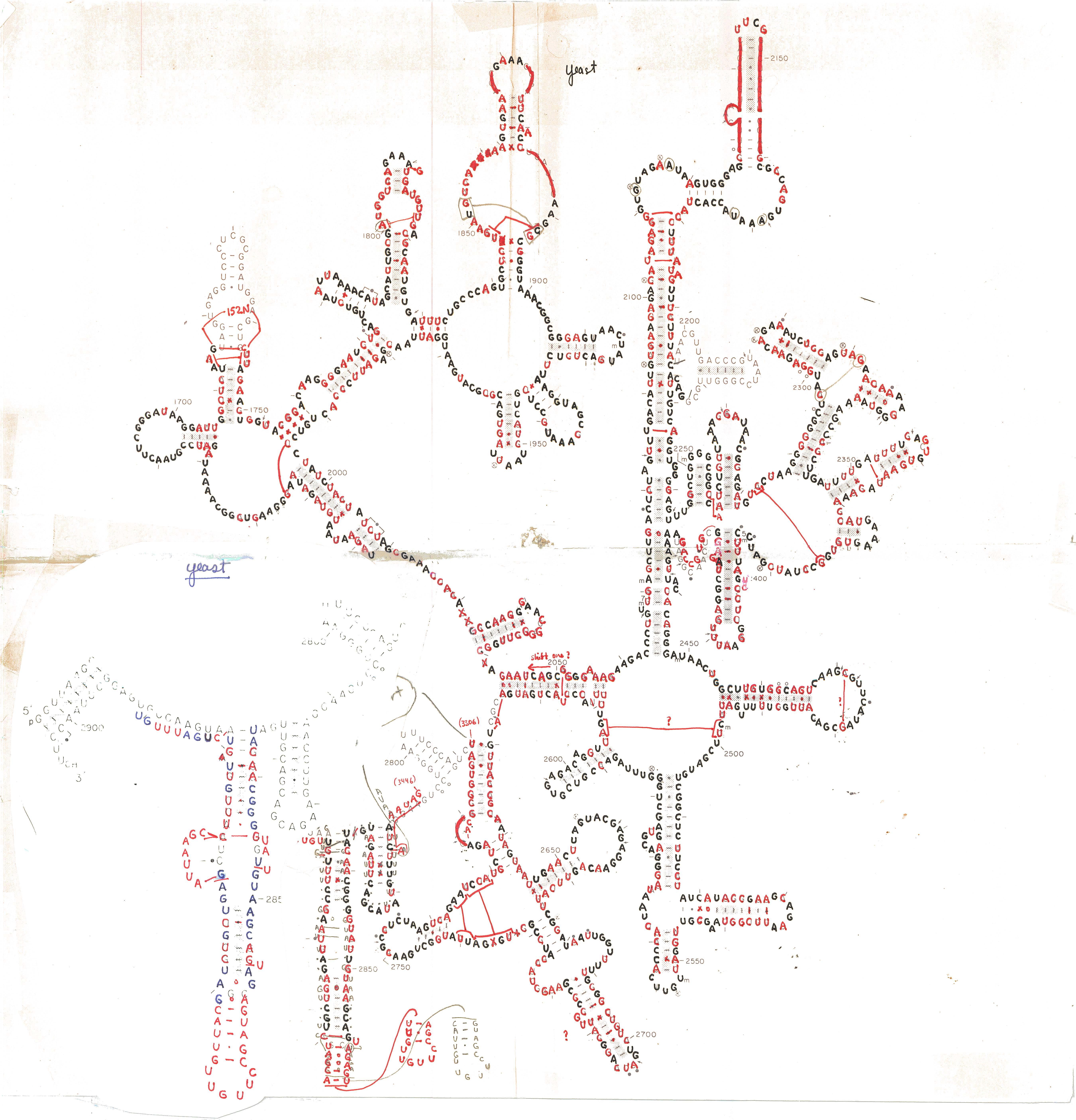


1e Modeling The Comparative Structure Of Ribosomal Rnas In The 1980s
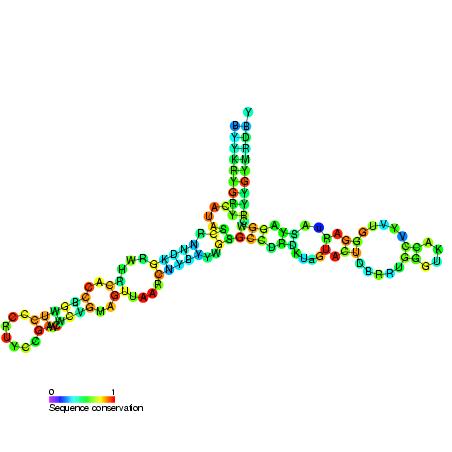


5s Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia



Figure 1 From Collection Of Small Subunit 16s And 16s Like Ribosomal Rna Structures Semantic Scholar
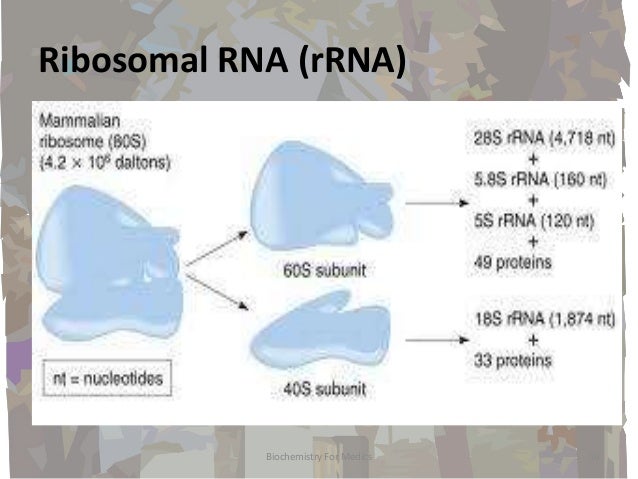


Rna Structures Types And Functions



Cryo Em Structure And Rrna Model Of A Translating Eukaryotic 80s Ribosome At 5 5 A Resolution Pnas



Nasa Astrobiology Institute
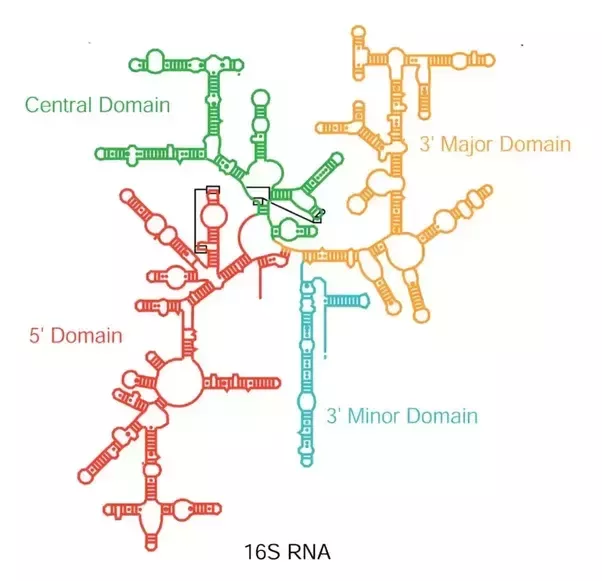


How Are The Shapes Of The Three Types Of Rna Described Quora
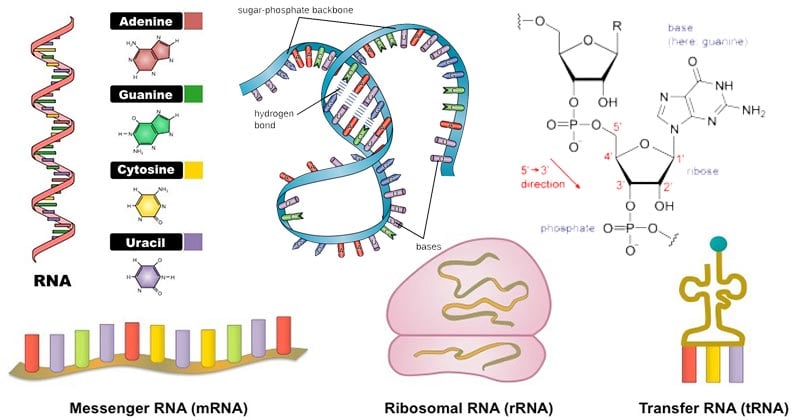


Rna Properties Structure Types And Functions Molecular Biology Microbe Notes



Crystal Structure Of A Conserved Ribosomal Protein Rna Complex Science
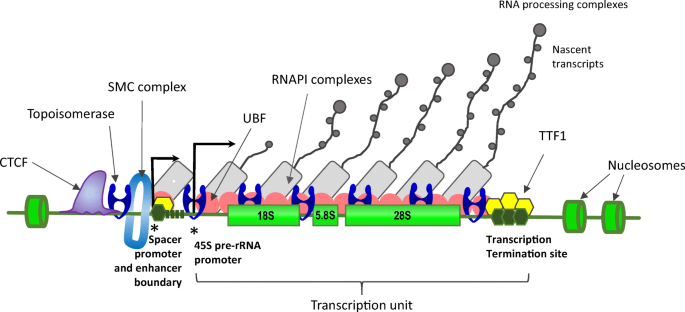


Ribosomal Dna And The Nucleolus In The Context Of Genome Organization Springerlink


Sulfolobus Acidocaldarius Ssu Rrna Secondary Structure Model
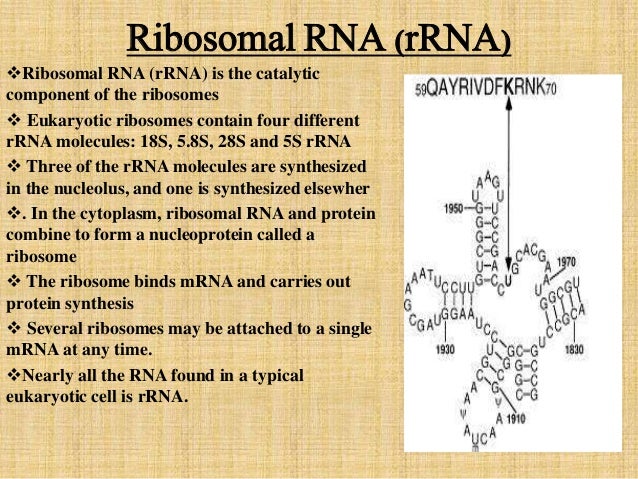


Structure Types And Function Of Rna
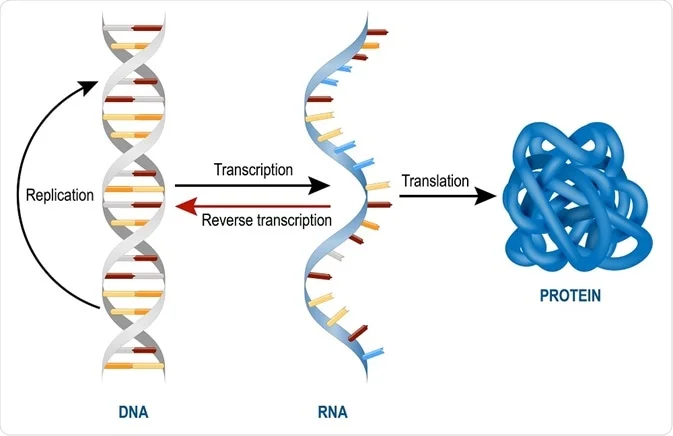


Types Of Rna Mrna Rrna And Trna
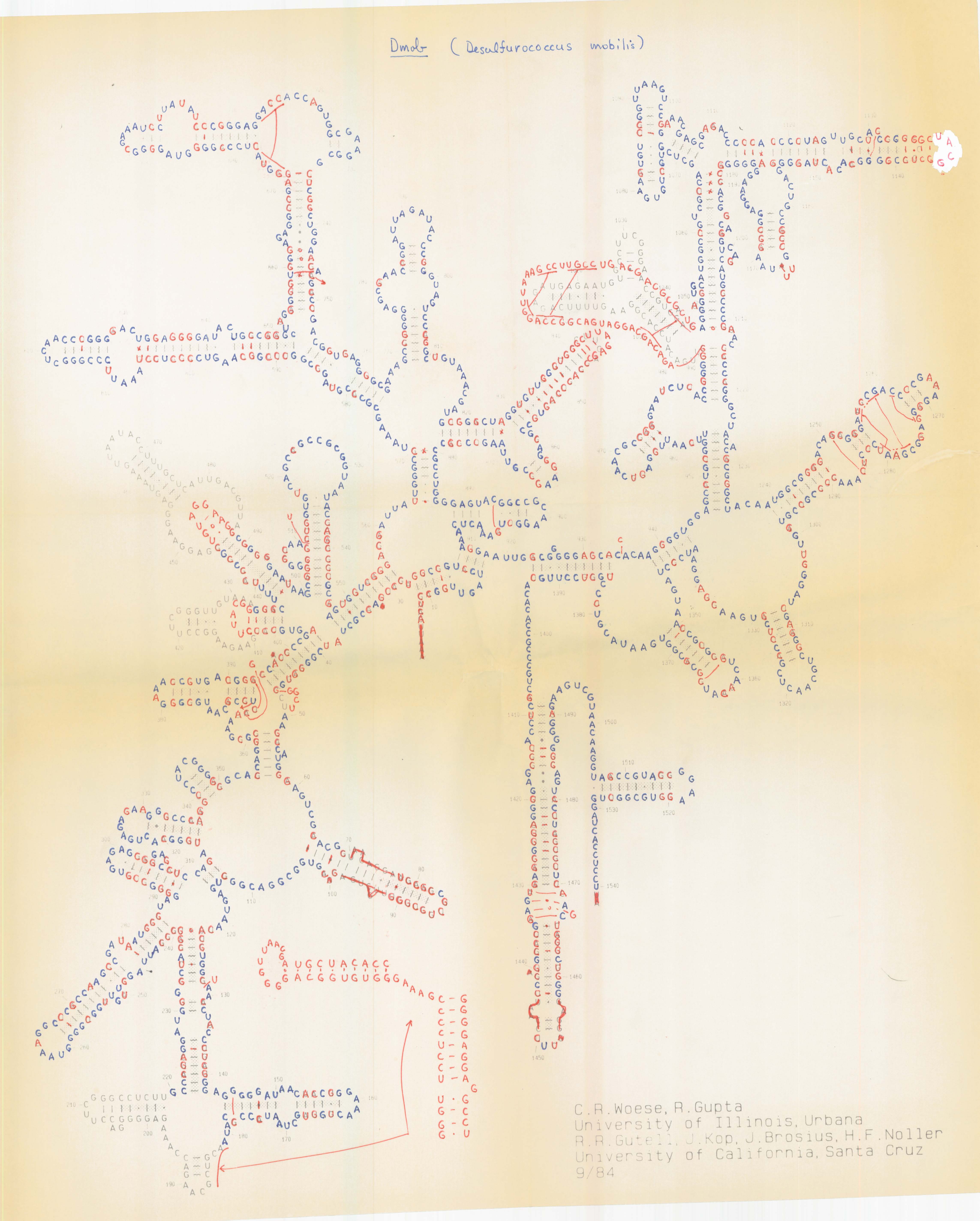


1e Modeling The Comparative Structure Of Ribosomal Rnas In The 1980s



Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology



Ribosomal Rna



Predicting And Visualizing 5s Rrna Structures Using Bioinformatics Tools To Help Students Learn Rna Structure And Function While Gaining Computer Research Skills Journal Of Chemical Education X Mol



Ribosomal Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Is The In Situ Accessibility Of The 16s Rrna Of Escherichia Coli For Cy3 Labeled Oligonucleotide Probes Predicted By A Three Dimensional Structure Model Of The 30s Ribosomal Subunit Applied And Environmental Microbiology



Xcqiuthlzsirvm



Ribosomal Rna Definition Function Britannica



Ribosomal Rna Wikipedia


Optimizing Gap Penalties In Clustal Intro To Ribosomal Rna


Ribosome Images


Q Tbn And9gcsnnf X7mag0luevkk4gakv Vo3vq G2ayf N2li1iynvfv Cgw Usqp Cau



Secondary Structure Model For E Coli 16s Rrna This Model Was Download Scientific Diagram


Rna Structure And Synthesis And Types Youtube


コメント
コメントを投稿